
Image credit: CyberTex
Cyber threats continue to be a critical issue in Africa as a result of our adoption of digital technologies in almost all of our sectors.
Positive Technologies, a leader in result-driven cybersecurity, has conducted research consisting of 29 African countries by analyzing dark web forums and telegram channels to produce cybersecurity findings about Africa during the first quarter of 2023 to the last quarter of 2024.
This article will share some of the key statistics you need to know.
Most targeted sectors in Africa
From Q1 2023 to Q3 2024, 89% of successful cyberattacks targeted African organizations, while 11% were directed at individuals.
Government agencies and financial organizations are the primary targets of cybercriminals in the region, accounting for 29% and 22% of all successful cyberattacks on organizations, respectively.
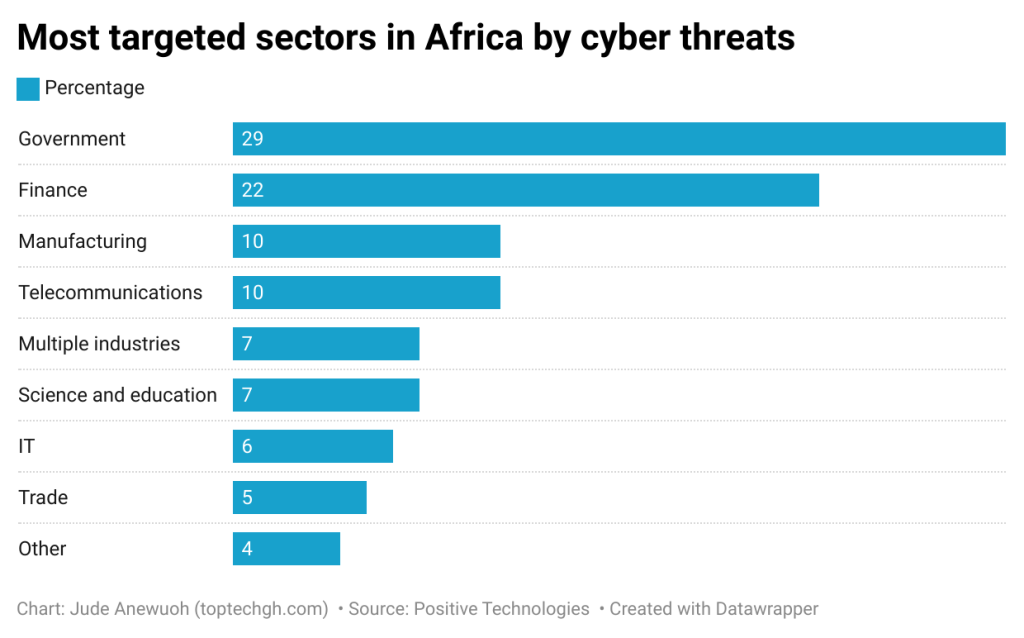
Cyberattacks on government agencies in the region are often perpetrated by APT groups (46%) and also hacktivists (18%). These groups primarily focus on long-term covert cyberattacks aimed at information collection and cyber espionage.
For instance, the Egyptian Ministry of Health and Population suffered a cyberespionage of a database containing 2 million records which was tagged for sale on a dark web forum according to positive technologies.
Data from dark web forums shows cybercriminals are most interested in the African government sectors of Nigeria (27%), Algeria (17%), Ethiopia (12%), and South Africa (12%).
Also, a dark web analysis by Positive Technologies shows the countries of greatest interest for cybercriminals are South Africa (25%), Nigeria (18%), and Algeria (13%). The dark web is a hidden part of the internet not indexed by regular search engines and accessible through dedicated browsers.
Also read: 5 Key Cybersecurity Controls for SMEs According to Expert
How do they attack?
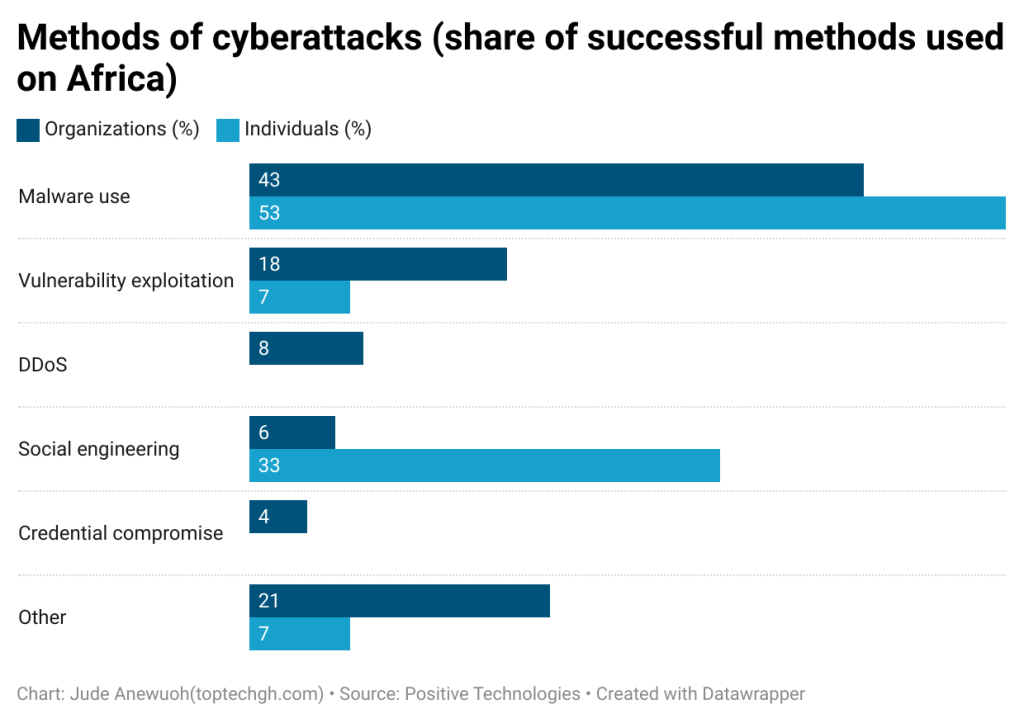
The most common method used by cyber attackers on organizations and individuals in Africa is Malware.
Malware recorded the most cases of attacks on organizations (43%) and individuals (53%).
When you take a closer look, the breakdown of malware types is as follows: Ransomware accounts for 29%, Spyware 25%, Remote Access Trojans (RATs) 20%, Loaders 17%, Miners 3%, and others make up the remaining 6%.
Other common methods include Vulnerability exploitation, DDoS, social engineering and credential compromise.
Effects of cyberattacks on the continent
Most cyberattacks on African countries led to a data breach — cybercriminals gaining access to confidential information. This effect significantly outpaced the remaining consequences on the organizational level (61%) and individual users (53%) as well.
Also read: South Africa, Nigeria, and Algeria Emerge as Top Targets on the Dark Web
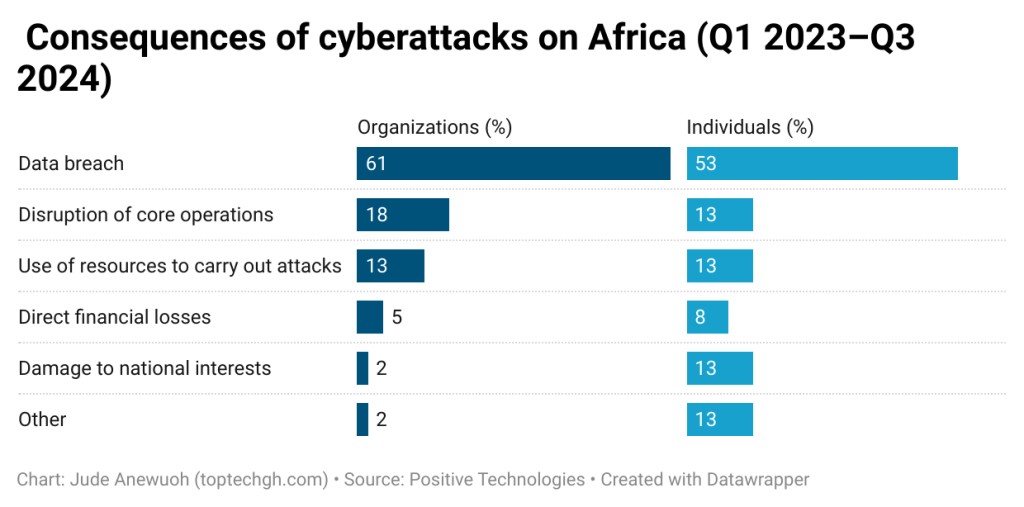
This aligns with SurfShark’s report on data breaches in Africa with Ghana ranked 9th for most cases in Africa.
To enhance cybersecurity in the region, experts at Positive Technologies recommend the following measures: strengthening the legal framework for cybersecurity, protecting critical information infrastructure, ensuring compliance with general cybersecurity requirements, promoting cooperation between government and businesses, fostering international cooperation with other countries, and providing employee training on cybersecurity.
Source: Positive Technologies




